Future Makers is a Nottingham-based creative studio who has been spending the last five years researching the potential of waste plastic, bringing together the local community, design creatives and artists to create innovative artwork and products.
Having recently acquired a whole set of waste plastic recycling and manufacturing equipment (which we have already started experimenting with), they announced an open call for a lead artist to craft an outdoor public artwork in front of their building, using one tonne of locally-sourced plastic waste.
The street facade of the existing Waste Plastic Studio (photo © Future Makers)
Our proposal
Continuing our exploration of community-built urban interventions in Nottingham, we responded to this open call with a diaphanous facade sculpture, to transform the Future Makers' building itself into a large art piece, and create a visually striking and intriguing street presence that hovers over the public space.
Questioning the ubiquitous nature of plastics in today's built environment and consumer society, the sculpture takes the form of a diaphanous mesh appearing to deform in and out of the building facades, to exude from the fabric of the building itself: the manifestation of the presence of plastics in a new, recycled form — and its metamorphosis from undesirable waste to creative potential. This large undulating sculptural mesh creates a unified identity across the site, linking the public space, the building entrance and the large industrial shed at the back.
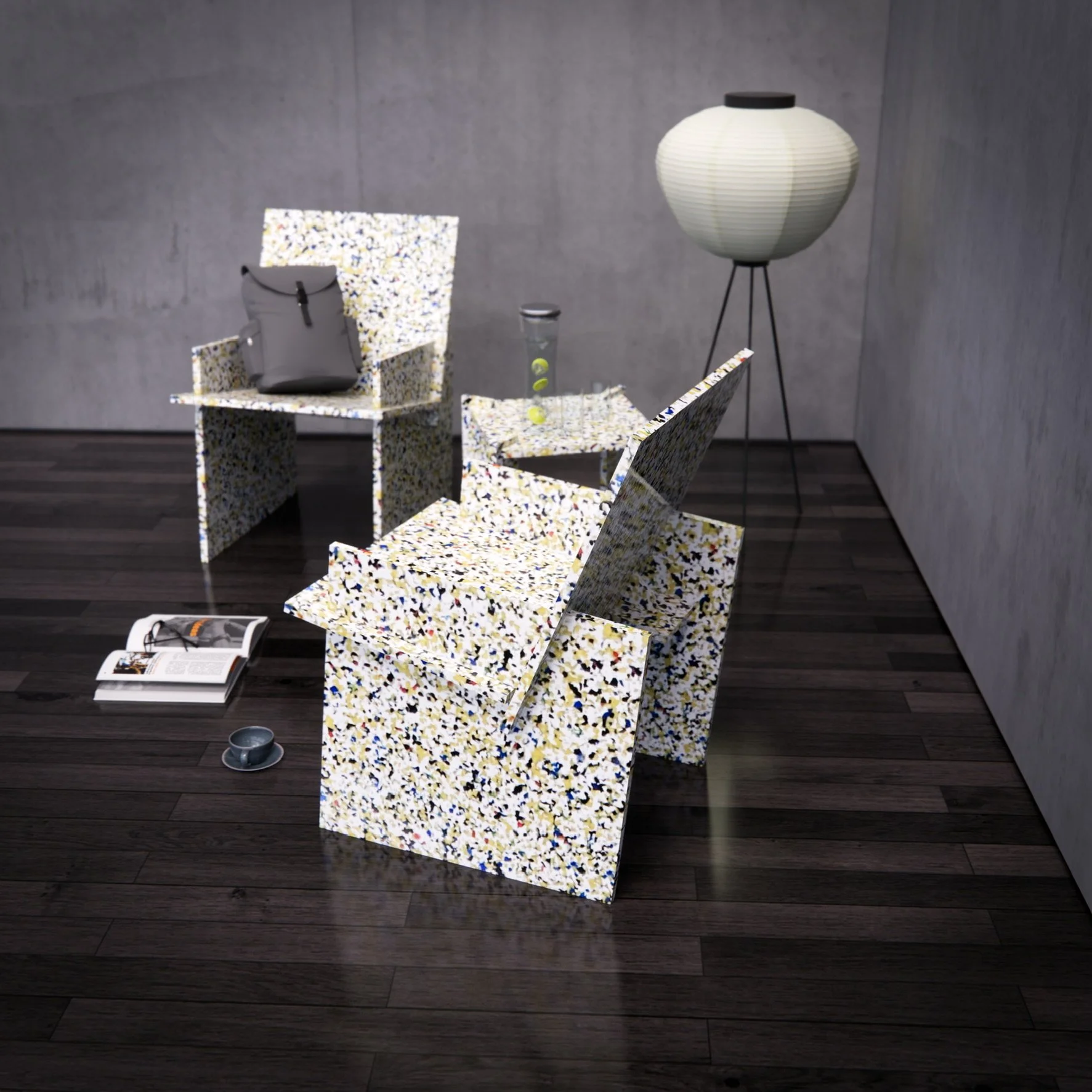
How we use recycled plastic
Despite its visual complexity, the mesh of the sculpture is created entirely out of identical recycled plastic modules, assembled in a repeating reciprocal pattern. The mesh derives its three-dimensional shape from the pattern of assembly of these modular components, linked together with a simple zip-tie-like "cilium" component.
Building the sculpture
The form of the sculpture emerges not from the complexity of its components, but from the assembly process itself: simply varying the pattern of assembly along the mesh allows shear, deformation and stiffening of the surface into a complex shape that symbolically intersects with the building's facades.
Assembling the sculpture is deceptively simple and can happen almost entirely on the ground, before being attached to the facades. The assembly and erection of the different sections of the sculpture will be carried out during community workshops involving neighbours, local schools and fellow artists, creating a sense of ownership while introducing a large audience to the potential of recycled plastics as a creative material, through practical, hands-on workshops.
Continuing our journey
Since its inception, 2hD has explored the relationship between architecture, visual arts and community engagement, through a series of successful international art projects ranging from architectural pavilions to collective sculptural work, interactive installations, scenography and audio-visual performances.
The common thread through all these different projects is our personal research into architectural elements as a receptacle for our own stories, emotions and daydreams, introducing a fractional dimension to surfaces to invite this projection — and exploring how, in turn, it affects how we perceive and inhabit the spaces they define.
This proposal also keys in with our love for reusing ubiquitous and repurposed materials: transformed cardboard boxes for collective community sculptures in The Lost Cuckoo, recycled plastic tubing to introduce school children and architecture students to complex geometries during hands-on teaching sessions, and natural fiber broom heads to clad an entire building for our Mission Control micro-office.